It is a signal that the instantaneous amplitude of the periodic signal repeatedly changes with time. Common periodic signals are: sinusoidal signals, pulse signals, and their rectification, differentiation, integration, and so on. This type of thing can be called a simple signal. They are characterized by no more than two extreme points in one cycle and a significant periodicity. For such signals with clear periodic characteristics, the periodicity is relatively simple, and the method of periodic measurement is also very mature, such as: zero-crossing detection method, pulse shaping method, etc.
x(t)=x(t+kT), k=1, 2. . . . .
Where t represents time and T represents cycle.
Spectrum conceptThe spectrum is an abbreviation for frequency spectral density and is a frequency distribution curve. The complex oscillation is decomposed into a resonant wave with different amplitudes and different frequencies. The pattern of the amplitudes of these resonant waves arranged in frequency is called the spectrum. The spectrum is widely used in acoustics, optics and radio technology. The spectrum introduces the study of the signal from the time domain to the frequency domain, resulting in a more intuitive understanding. The spectrum in which complex mechanical vibration is decomposed is called a mechanical vibration spectrum, the spectrum in which sound vibration is decomposed is called a sound spectrum, the spectrum in which optical vibration is decomposed into a spectrum is called a spectrum, and the spectrum in which electromagnetic vibration is decomposed into a spectrum is called an electromagnetic spectrum. It is common to include the spectrum within the range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Analysis of the spectrum of various vibrations can understand many of the fundamental properties of this complex vibration, so spectrum analysis has become a basic method for analyzing various complex vibrations.
(1) Discreteness: The spectral lines are discrete.
(2) Convergence: The total trend of harmonic amplitude decreases as the number of harmonics increases.
(3) Harmonicity: The spectral line only appears at a frequency that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency.
Effective spectral width of the periodic signalIn the spectrum analysis of periodic signals, the spectrum of periodic rectangular pulse signals has a typical meaning and is widely used. Taking the periodic rectangular pulse signal shown in Figure 3-8 as an example, the relationship between the spectrum width and the pulse width is further studied.
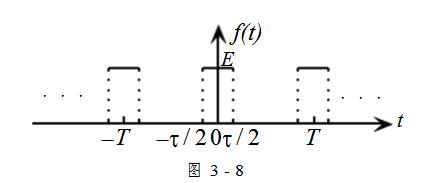
Figure 3-8 shows the signal) (the pulse width of tf is 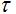 , the pulse amplitude is E, the repetition period is T, and the repetition angle frequency is
, the pulse amplitude is E, the repetition period is T, and the repetition angle frequency is 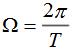
If (ff is expanded to the Fourier series of equation (3-17), then equation (3-18) is available.
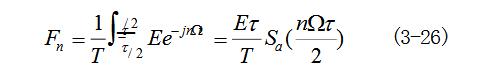
Here Fn is a real number. Therefore, the amplitude spectrum and the phase spectrum are generally combined in one picture, as shown in Figure 3-9.
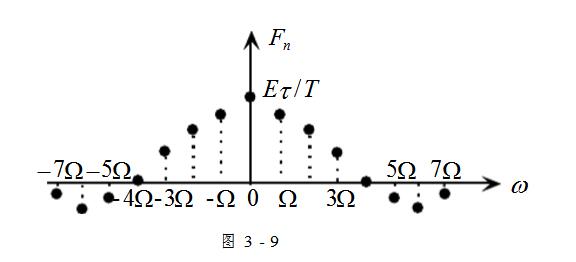
This figure shows that:
(1) The spectrum of the periodic rectangular pulse signal is discrete, and the two spectral line spacing is 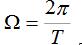
(2) The magnitude of the DC component, the fundamental wave and each harmonic component is proportional to the pulse width E and the pulse width. 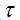 , inversely proportional to the period T, the change is affected by the envelope
, inversely proportional to the period T, the change is affected by the envelope 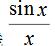 The containment.
The containment.
(3) When 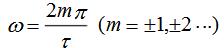 When the line's envelope crosses zero. therefore
When the line's envelope crosses zero. therefore 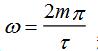 It is called the zero component frequency.
It is called the zero component frequency.
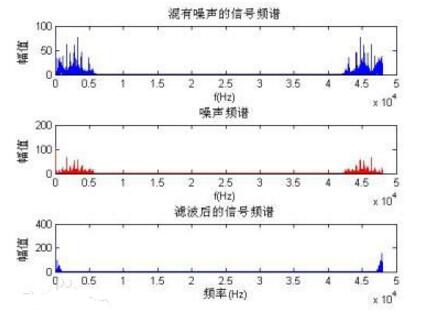
(4) The periodic rectangular pulse signal contains an infinite number of spectral lines, which can be decomposed into an infinite number of frequency components, but the main energy is concentrated within the first zero component frequency. Therefore, this frequency range is usually called the effective spectrum width of the rectangular signal or the occupied frequency band of the signal, which is recorded as or
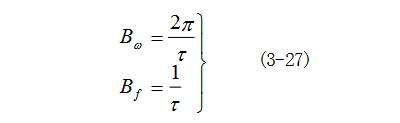
Obviously, the effective spectrum width B is only with the pulse width 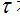 Related, and inversely related. The effective spectral width is an important part of studying the signal and system frequency characteristics. To make the signal undistorted through the linear system, the frequency characteristics of the system itself must be adapted to the bandwidth of the signal.
Related, and inversely related. The effective spectral width is an important part of studying the signal and system frequency characteristics. To make the signal undistorted through the linear system, the frequency characteristics of the system itself must be adapted to the bandwidth of the signal.
For a general periodic signal, a discrete spectrum is also obtained, and there is also a zero component frequency and an occupied frequency band of the signal.
Relationship between periodic signal spectrum and period TThe following is still an example of the periodic rectangular signal shown in Figure 3-8. because
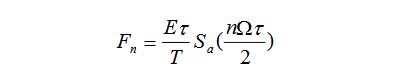
Therefore, if the pulse width ï´ remains the same, if the period T is increased, it can be seen that:
(1) Interval of discrete lines 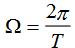 It will become smaller, that is, the line will become dense.
It will become smaller, that is, the line will become dense.
(2) The amplitude of each line will become smaller, and the envelope changes slowly, that is, the amplitude convergence speed becomes slower.
(3) due to 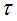 It is unchanged, so the zero component frequency position is unchanged, and the effective spectrum width of the signal is also unchanged.
It is unchanged, so the zero component frequency position is unchanged, and the effective spectrum width of the signal is also unchanged.
Fork Type Connecting Terminals
Fork Type Connecting Terminals,Terminals,Connecting Terminals
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyiterminals.com