The BeiDou Naviga Satellite Satellite System (BDS) is a self-developed, independently operated global satellite navigation system being implemented in China. Beidou Satellite Navigation is committed to providing high quality positioning, navigation and timing services to users around the world, including free positioning, speed and timing services worldwide. At present, the construction of the Beidou satellite system is progressing steadily as planned. At present, 16 Beidou navigation satellites have been successfully launched, covering the Asia-Pacific region.
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) is a wireless network composed of a large number of stationary or mobile sensors in a self-organizing and multi-hop manner to collaboratively sense, collect, process and transmit the perceived objects in the network coverage geographic area. Information and ultimately send this information to the owner of the network. Among the wireless sensor network technologies, ZigBee technology is the most suitable for low power consumption, low cost, and high reliability. ZigBee technology is a wireless communication technology that operates on three frequency bands in the world, the United States and Europe, based on wireless communication protocols. It has the characteristics of low power consumption, low cost, low complexity and automatic networking. It is mainly suitable for short-range wireless communication, networking, automatic control and remote control, and can be embedded in various devices.
These two popular technologies have distinct characteristics. If they are combined, the combination of positioning and navigation technology and short-distance networking technology can realize wider and more complex applications, satisfying detection, positioning, navigation, etc. for different scales and requirements. Various needs, convenient data transmission, to make up for the gaps in existing technology products.
1 innovative features
1.1 Precise positioning
ZigBee nodes are widely used in field environment surveys, intelligent traffic monitoring, etc. The data collected by simple ZigBee nodes is one-dimensional data, and isolated data is not conducive to analysis and decision-making. If the location information of the collection location is also acquired together, the collected environmental information can be combined with the location information, and drawn into a two-dimensional data map during aggregation and analysis, and the distribution of the information can be intuitively understood; If you add precise time, you will form a three-dimensional data body, which is more comprehensive and comprehensive.
1.2 Indirect positioning
Satellite positioning is usually required to be outdoors in the sky, so it is difficult to locate indoors. With the indirect positioning of ZigBee, when a ZigBee network containing positioning devices already exists, the ZigBee network can be accessed for indirect positioning. It is equivalent to providing real-time indirect positioning services in any area where the network can be accessed in this area. Any device can obtain its current location information through the ZigBee network, which not only reduces the cost of the positioning service, but also expands the positioning. Application range.
1.3 Network timing
Although ZigBee network has the advantages of low cost, low power consumption and high reliability, considering the network delay and low data transmission rate, the system real-time performance is not satisfactory. When the ZigBee network is faced with an application that requires high real-time performance, it is bound to affect the accuracy of the data due to the large delay. If the precise time obtained from the Beidou satellite navigation system is used, and then all the nodes in the whole network are calibrated, the synchronization of the nodes is improved, thereby improving the response speed of the system.
1.4 Data Communication
Although the Beidou satellite navigation system can provide accurate time and location information, but there is no information transmission capability, the ZigBee network provides an easy way for this information organization. By locating the Beidou positioning data in the ZigBee network, location information can be transmitted.
2 System design of Beidou+ZigBee terminal
2.1 Structural system
The Beidou navigation system and the ZigBee network structure system are shown in Figure 1. They are mainly composed of ZigBee network nodes and Beidou navigation nodes. The sensor network subnet usually consists of one master node and multiple nodes. The master node is mainly responsible for the management of the networking and intranet devices of the ZigBee network, and communicates with the Beidou positioning navigation module.
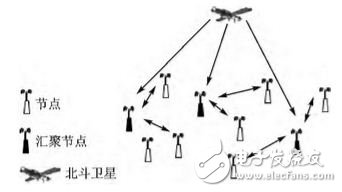
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of Beidou-ZigBee network structure
2.2 Hardware Design
In the design of the ZigBee node, the MC13213 chip introduced by Freescale for ZigBee technology was selected. The chip is a complete single-chip solution with an integrated HCS 08 MCU and a second-generation wireless RF transceiver that complies with the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, also known as Modem. The MC13213 is capable of building powerful network nodes at very low total material costs. It is characterized by fast speed and abundant resources on the chip. Its hardware block diagram is shown in Figure 2.
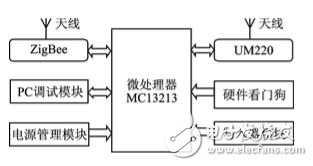
Figure 2 terminal hardware functional block diagram
The Beidou positioning navigation module is designed with Core Star's UM220 chip as its core. The UM220 is a Beidou/GPS dual system module for applications such as vehicle monitoring, weather detection and telecom power timing. The single chip supports the Beidou BD2/GPS function, which can directly output NMEA data without an external CPU, and supports various interfaces such as UART, SPI, 1PPS, and I2C. The pin connection is shown in Figure 3. This design is connected to PTE1 (TXD1) and PTE0 (RXD1) of MC13213 through TXD3 and RXD3 respectively to realize data communication.
Figure 3 UM220 and MC13213 connection diagram
2.3 Software Design
ZigBee is a low-power personal area network protocol based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. According to the technology specified in this agreement, it is a short-distance, low-power wireless communication technology. ZigBee devices include the PHY and MAC layers of IEEE 802.15.4 (which defines RF radio and communication with neighboring devices), and the ZigBee stack layer - Network Layer (NWK), Application Layer, and Security Service Provisioning Layer.
Due to the limitation of wireless transmission power consumption, the transmission effective distance is less than 100 m. Therefore, for the coverage in the area, automatic networking and path calculation functions need to be implemented through the built-in ZigBee protocol stack. In the terminal design, the carrier medium for data transmission is a ZigBee network. Whether it is precisely positioned coordinate information, indirectly located detection information, or time-synchronized data, it relies on the data service provided by ZigBee for transmission.
The precise positioning function relies on the precise coordinates obtained by Beidou navigation positioning. The UM220 module provides positioning information for the Beidou. The UM220 output data adopts ASCII code and performs asynchronous serial communication according to the NMEA-0183 format. Therefore, by connecting it to the MC13213 through the serial port, the positioning information is output once per second, and the positioning information is processed by the built-in single chip of the MC13213. The UM 220 output statement has $BDGGA, $BDGSA, $BDGSV, $BDRMC, and so on. The $BDGGA positioning data statement is the most commonly used statement, so we use it as the output statement for positioning information.
The $BDGGA statement consists of 17 fields: statement identifier header, world time, latitude, latitude hemisphere, longitude, longitude hemisphere, positioning quality indication, number of satellites used, horizontal accuracy, altitude, altitude unit, geoid height, height unit , differential GPS data duration, differential reference base station label, checksum end marker (with carriage return and line feed), separated by 14 commas. This gives accurate information on the latitude, longitude and altitude. This information will be stored in the memory of the MC13213, which not only realizes the precise positioning of the nodes, but also provides reference information for the indirect positioning of other nodes as its own location information.
There are two commonly used algorithms for indirect positioning: distance-based positioning algorithms and distance-independent positioning algorithms. The advantage of the distance-independent positioning algorithm is that the hardware structure requirements of the node are low; the disadvantage is that the positioning accuracy is not high, and it is difficult to meet the accuracy requirements of indoor positioning. Distance-based positioning is performed by measuring point-to-point distance or angle information between nodes, and then calculating the node position using a certain calculation method. Commonly used ranging technologies include RSSI, TOA, TDOA, and AOA. Since the ZigBee wireless communication module can directly provide the RSSI value, the design uses the RSSI information to implement the positioning function.
To measure distance using RSSI, a model of distance and RSSI needs to be established. Since the empirical model needs to simulate the test environment before the actual positioning, and establish an offline database of the position and signal strength relationship at various distances in the environment, the operation is cumbersome, and the database is not suitable for the application of the single chip microcomputer. Therefore, the theoretical model is adopted here. The calculation is performed using a radio propagation path loss model.
The free space radio propagation path loss model formula is as follows:
Loss = 32.44 + 10klog10d + 10klog10f (1)
Where d is the distance of the receiving point from the source, the unit is km; f is the frequency, the unit is MHz; k is the path attenuation factor.
In the actual application environment, the model is improved due to various influences such as multipath, diffraction, and obstacles. Here a log-normal distribution model is used, which is calculated as:
In the formula, Xσ is a Gaussian distribution random variable with an average value of 0, and the standard deviation ranges from 4 to 10; k ranges from 2 to 5. Taking d=1, substituting into equation (1) can obtain the value of Loss, that is, PL(d0). Therefore, the signal strength formula of the unknown node receiving the anchor node signal is as follows:
RSSI = Transmit Power + Antenna Gain - Path Loss (PL(d))
It is assumed that the mobile node 0 receives the signals transmitted by n (n ≥ 3) fixed nodes, and selects the three fixed nodes with the strongest received signals as the beacon nodes A, B, and C from the received n signals. Using the RSSI ranging method, the measured distances are dA, dB, and dC, respectively, and the position can be determined by the three-sided measurement method shown in FIG. 4 according to dA, dB, and dC. If you don't intersect at one point, you can do it according to the centroid method.
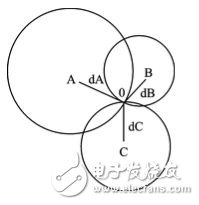
Figure 4 Trilateral measurement
In theory, although the information of three located nodes can be obtained to determine the location of an unknown node, the actual situation will be biased due to interference. For example, when an unexpected obstruction occurs between two RFs, the received signal is reduced by 30 dBm. In order to correct the anomaly and improve the accuracy of the positioning result, the indirect positioning needs as many RSSI values ​​of the located nodes as possible, and performs related positioning calculations. Then, when a large number of nodes are used, the RSSI value will tend to be stable. More accurate positioning results can be obtained.
The time synchronization of ZigBee network is realized by FTSP algorithm. It implements one-to-one or one-to-many time synchronization by sending a message and timestamping both the sending and receiving ends. The FTSP algorithm provides multi-hop time synchronization. A root clock is maintained by the root node of the network, and all other nodes are synchronized to the root node, thereby synchronizing all nodes in the entire network.
The implementation steps of the FTSP algorithm are as follows:
1 Transmit sync (sync) byte, calculate the timestamp t, the calculation method is the current time minus the transmission time of the message data part, and the transmission time of the message data part can be obtained by the data length and the transmission rate. Transmit timestamp t.
2 Receive the data packet, record the time tr of the last arrival of the sync byte, and calculate the bit offset. After receiving the complete message, the time delay tb generated by the bit offset is calculated by calculating the bit offset and the receiving rate.
3 The receiving node calculates a clock offset off-set between the transmitting node and then adjusts the local clock to synchronize with the clock of the transmitting node.
3 performance test
3.1 Positioning error test
In the actual test of indirect positioning, a total of 23 sensing nodes were deployed, of which 11 were directly positioned using Beidou, and 12 were located without ZigBee positioning. The nodes are randomly distributed, and the distances between the nodes are set to 10 to 20 m, and then 10 indirect positioning experiments are performed. The error between the actual measured value and the actual measured value is analyzed by statistical data, and the result is shown in FIG. 5.
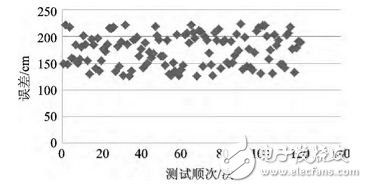
Figure 5 Indirect positioning error distribution
Based on the comprehensive calculation, the average positioning error of 10 experiments was 1.7 m. Considering the average distance between nodes of 14 m, the positioning error is small and meets the application requirements.
3.2 Time synchronization error test
In the time-synchronized simulation, the nodes in the indirect positioning test are still used. The 23 nodes are randomly distributed, and the time synchronization period is 5 s. Some functions of the module are added in the original ZigBee protocol, including the time stamp of the MAC layer. In the experiment, the average synchronization error of single-hop and multi-hop between nodes in the network was recorded, and the number of tests was 10 times. The experimental results are shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Indirect positioning error distribution
According to the experimental results, the average error of the single-hop FTSP of the two nodes is 2.12μs; but the average error of the two nodes and the FTSP is 11.97 μs when the 7-hop is obtained. The results show that the accuracy of the synchronization error of the FTSP algorithm in multi-hop networks is better. High, smooth curve, meet the requirements, can achieve the purpose of improving the time synchronization accuracy of ZigBee network.
4. Conclusion
Utilizing the hardware and software platform of Freescale's ZigBee communication module MC13213 and Hexinxing UM220 positioning and navigation chip, the positioning information and timing function of Beidou satellite positioning system are combined with ZigBee system; ZigBee is improved by using accurate positioning and timing data. The performance of the protocol stack enhances the functionality of its nodes, enabling precise positioning, indirect positioning, and time-to-network synchronization improvements. Through the advantages of ZigBee network transmission performance, it makes up for the lack of liquidity and data form isolation of a single Beidou navigation data. After testing, the design terminal has stable performance and good results, and has achieved the expected design goals.
Best Tower Speaker,Tower Speakers For Sale,Soundlogic Tower Speaker,Tower Speakers With Mic
Newmax Electronics Co.,LTD , https://www.fspeaker.com